- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping

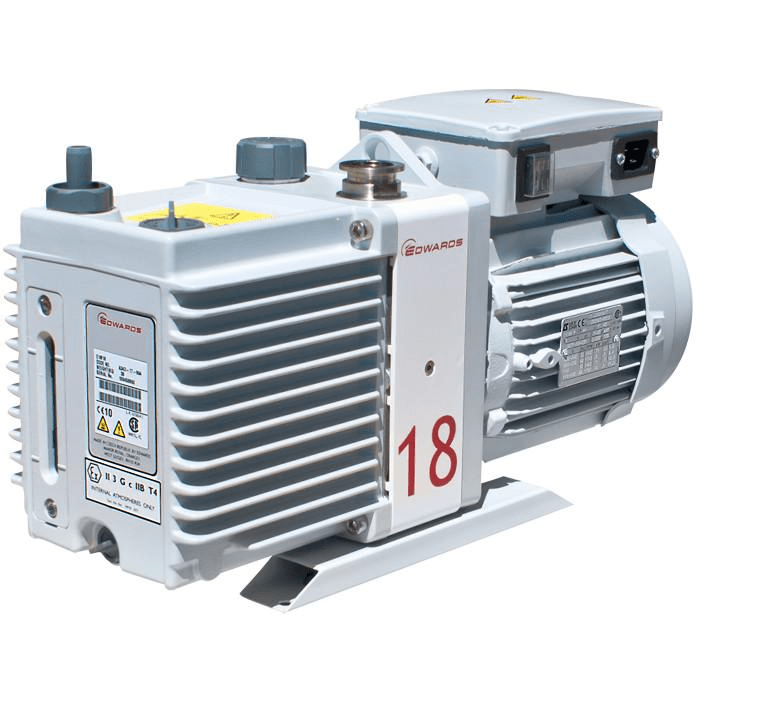
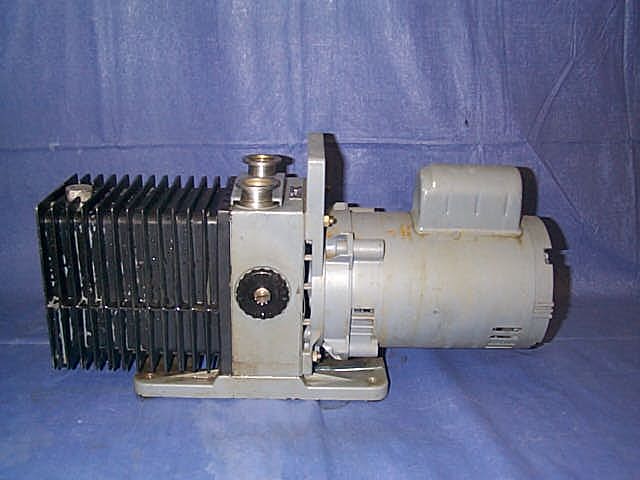
Product
Vacuum pumps are used in many industrial and scientific processes including:
- The production of most types of electric lamps, vacuum tubes, and and CRTs where the device is either left evacuated or re-filled with a specific gas or gas mixture
- Semiconductor processing, notably ion implantation and sputter deposition
- Electron microscopy
- Medical processes that require suction
- Mass spectrometers to create an ultra high vacuum between the ion source and the detector
- Vacuum engineering
Vacuum may be used to power mechanical devices. In diesel-engined automobiles, a pump fitted on the engine (usually on the camshaft) is used to produce vacuum. In gasoline-powered automobiles, instead, vacuum is obtained as a side-effect of the operation of the engine and the flow restriction created by the throttle plate. This vacuum may then be used to power:
- The booster for the power brakes
- Motors that move dampers in the ventilation system
- The throttle driver in the cruise control servomechanism
- Controlling other devices (such as turbo geometry, EGR, etc.)
In an aircraft, the vacuum source is often used to power gyroscopes in the various flight instruments. To prevent the complete loss of instrumentation in the event of an electrical failure, the instrument panel is deliberately designed with certain instruments powered by electricity and other instruments powered by the vacuum source.